
JAVA MEANING IN COMPUTER LANGUAGE SOFTWARE
Creating a domain-specific language (with software to support it), rather than reusing an existing language, can be worthwhile if the language allows a particular type of problem or solution to be expressed more clearly than an existing language would allow and the type of problem in question reappears sufficiently often.
Language-oriented programming considers the creation of special-purpose languages for expressing problems as standard part of the problem-solving process. The design and use of appropriate DSLs is a key part of domain engineering, by using a language suitable to the domain at hand – this may consist of using an existing DSL or GPL, or developing a new DSL. By contrast, PostScript is a Turing-complete language, and in principle can be used for any task, but in practice is narrowly used as a page description language. For example, Perl was originally developed as a text-processing and glue language, for the same domain as AWK and shell scripts, but was mostly used as a general-purpose programming language later on. The line between general-purpose languages and domain-specific languages is not always sharp, as a language may have specialized features for a particular domain but be applicable more broadly, or conversely may in principle be capable of broad application but in practice used primarily for a specific domain. Simpler DSLs, particularly ones used by a single application, are sometimes informally called mini-languages. Special-purpose computer languages have always existed in the computer age, but the term "domain-specific language" has become more popular due to the rise of domain-specific modeling. DSLs can be further subdivided by the kind of language, and include domain-specific markup languages, domain-specific modeling languages (more generally, specification languages), and domain-specific programming languages. There are a wide variety of DSLs, ranging from widely used languages for common domains, such as HTML for web pages, down to languages used by only one or a few pieces of software, such as MUSH soft code. This is in contrast to a general-purpose language (GPL), which is broadly applicable across domains.
JAVA MEANING IN COMPUTER LANGUAGE PORTABLE
Java was written to be a portable and cross-platform language that doesn't care about the operating system, hardware, or devices that it's running on.Computer language specialized to a particular set of requirements or functionalityĪ domain-specific language ( DSL) is a computer language specialized to a particular application domain. Platform Independence: Programs need to work regardless of the machines they're being executed on.Java is probably the most secure programming language to date. Security: Because Java was originally targeting mobile devices that would be exchanging data over networks, it was built to include a high level of security.When data and its manipulation were packaged together in one place, Java was robust. With this in mind, object-oriented programming was introduced. Reliability: Java needed to reduce the likelihood of fatal errors from programmer mistakes.Java built on and improved the ideas of C++ to provide a programming language that was powerful and simple to use.
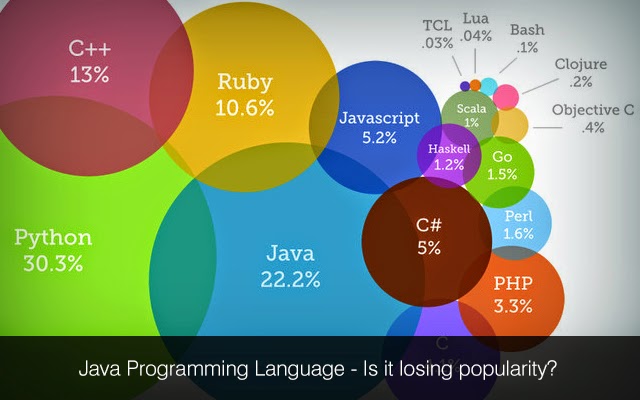
Although C++ is a powerful language, it is complex in its syntax and inadequate for some of Java's requirements. Ease of Use: The fundamentals of Java came from a programming language called C++.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
